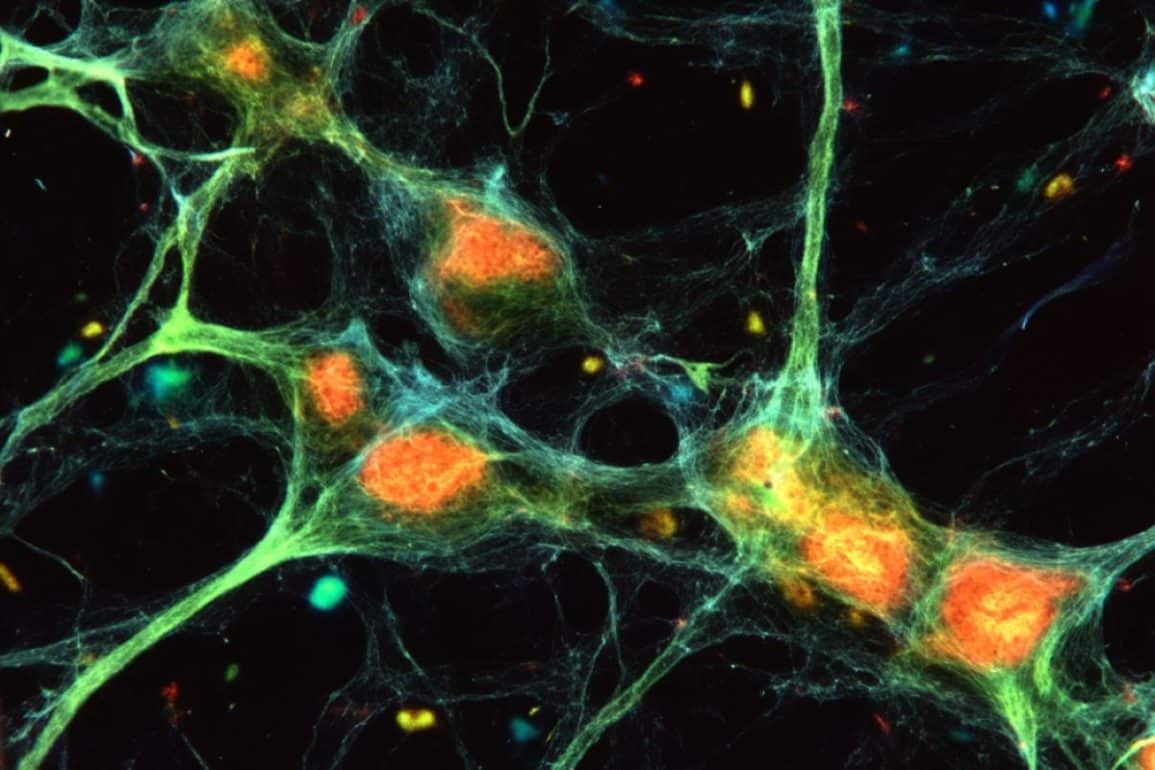
Emerging research suggests that chronic inflammation, rather than neurotransmitter deficiencies alone, may be a major factor behind depression, reshaping traditional views of the condition. This insight links inflammation, both in the body and brain, to depressive symptoms, explaining why some patients don't respond to conventional antidepressants. Studies reveal that stress can trigger immune responses that activate and later damage microglial cells in the brain, worsening depressive symptoms over time.
 Researchers have developed an innovative CAR T-cell therapy to combat glioblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor in adults. This approach not only attacks tumor cells directly but also reprograms the tumor's microenvironment, enabling immune cells to fight the cancer rather than protect it.
Researchers have developed an innovative CAR T-cell therapy to combat glioblastoma, the most common malignant brain tumor in adults. This approach not only attacks tumor cells directly but also reprograms the tumor's microenvironment, enabling immune cells to fight the cancer rather than protect it.