New research links childhood adversity with later attention deficits, sleep disruptions, and specific dopamine imbalances in the brain. Focusing on critical developmental windows, scientists found that disrupted care early in life affected males more than females.
New research links childhood adversity with later attention deficits, sleep disruptions, and specific dopamine imbalances in the brain. Focusing on critical developmental windows, scientists found that disrupted care early in life affected males more than females. Reading view
Emotional Bonding: How Dog-Owner Heart Rates Sync During Interaction
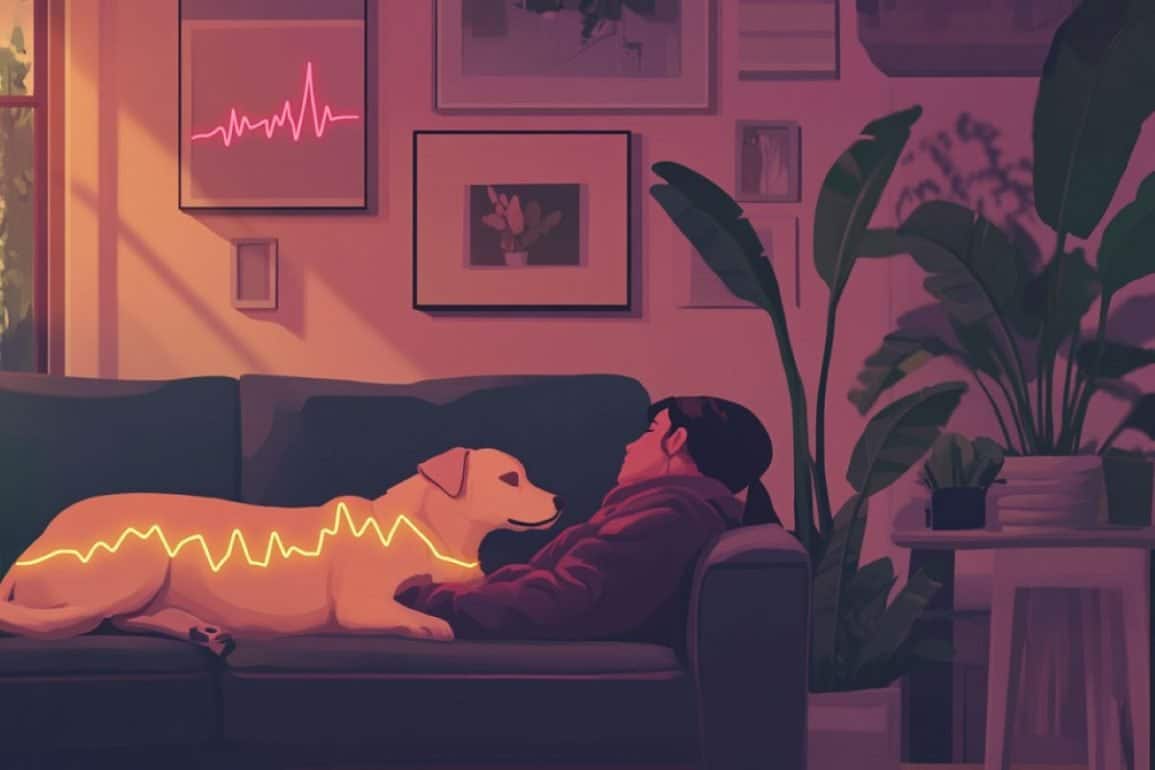 Dogs and their owners show synchronized heart rate variability (HRV), reflecting shared emotional states during relaxed interactions, a new study reveals. Researchers observed that both heart rate and physical activity levels adapt between dogs and owners, but the strongest emotional connection appears during restful moments, indicating shared relaxation.
Dogs and their owners show synchronized heart rate variability (HRV), reflecting shared emotional states during relaxed interactions, a new study reveals. Researchers observed that both heart rate and physical activity levels adapt between dogs and owners, but the strongest emotional connection appears during restful moments, indicating shared relaxation. Chimpanzees’ Task Performance Changes When Observed by Humans
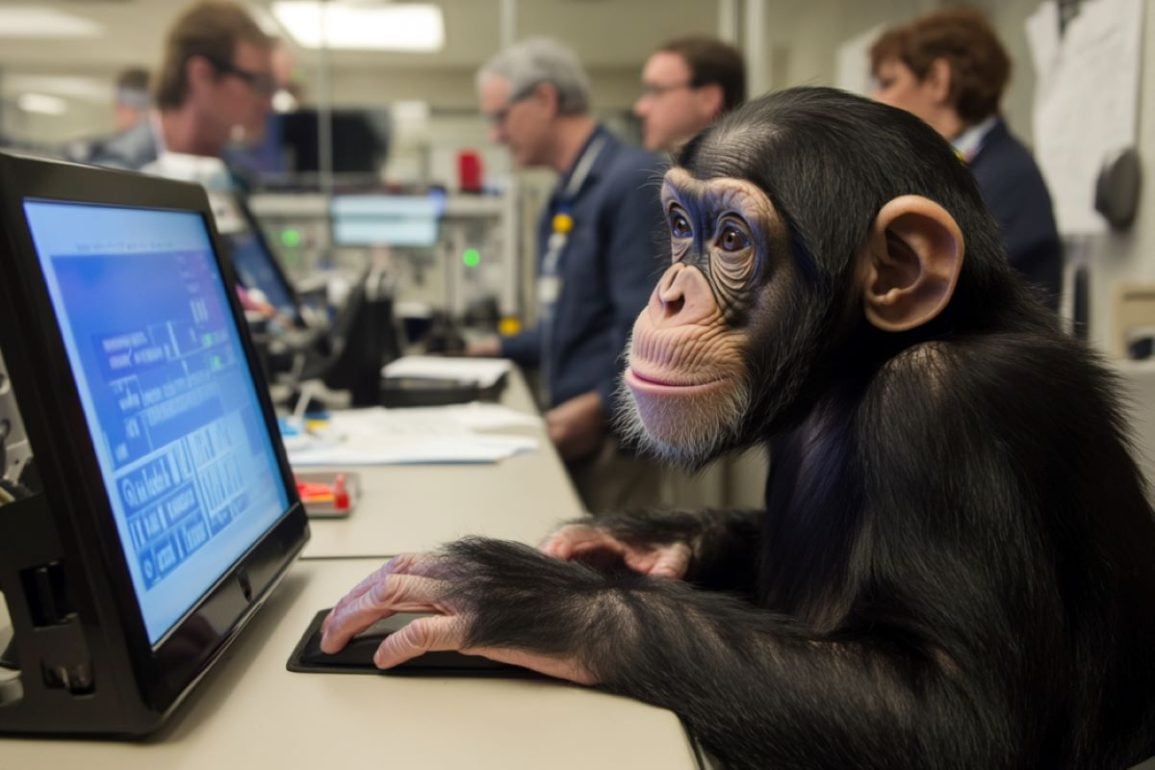 A new study finds that chimpanzees, like humans, are affected by being watched: their performance on computer tasks improved on difficult tasks with larger human audiences but declined on simpler ones. This phenomenon, known as the "audience effect," was previously thought to be unique to humans and linked to reputation management. The results suggest that sensitivity to being observed may have evolved before human society developed its complex reputation-based social structures.
A new study finds that chimpanzees, like humans, are affected by being watched: their performance on computer tasks improved on difficult tasks with larger human audiences but declined on simpler ones. This phenomenon, known as the "audience effect," was previously thought to be unique to humans and linked to reputation management. The results suggest that sensitivity to being observed may have evolved before human society developed its complex reputation-based social structures. Gut Bacteria Modulate Stress Responses Over Time
 New research has unveiled how gut bacteria play a key role in regulating stress by interacting with circadian rhythms, opening possibilities for microbiome-based therapies for mental health. Researchers found that depletion of certain gut bacteria can lead to time-specific increases in stress responses through the HPA axis, the body's central stress response system. Specific bacteria, such as Limosilactobacillus reuteri, were identified as crucial to modulating stress hormones throughout the day.
New research has unveiled how gut bacteria play a key role in regulating stress by interacting with circadian rhythms, opening possibilities for microbiome-based therapies for mental health. Researchers found that depletion of certain gut bacteria can lead to time-specific increases in stress responses through the HPA axis, the body's central stress response system. Specific bacteria, such as Limosilactobacillus reuteri, were identified as crucial to modulating stress hormones throughout the day. Childhood Attention Problems and Genes Linked to Psychosis Risk
 Childhood attention issues, coupled with genetic predispositions, increase the likelihood of experiencing psychotic-like symptoms in adolescence. By analyzing data from 10,000 youths, researchers discovered that variability in attention spans partially explains how genetic risk factors translate into psychotic-like symptoms.
Childhood attention issues, coupled with genetic predispositions, increase the likelihood of experiencing psychotic-like symptoms in adolescence. By analyzing data from 10,000 youths, researchers discovered that variability in attention spans partially explains how genetic risk factors translate into psychotic-like symptoms. Prenatal Cannabis Use Linked to Child Aggression and Cognitive Deficits
 Prenatal exposure to cannabis can negatively impact children’s thinking and behavioral skills, including impulse control, attention, and aggression, which are key for academic and social success. The study observed preschool-aged children with prenatal cannabis exposure and found they showed poorer control over impulses and emotions.
Prenatal exposure to cannabis can negatively impact children’s thinking and behavioral skills, including impulse control, attention, and aggression, which are key for academic and social success. The study observed preschool-aged children with prenatal cannabis exposure and found they showed poorer control over impulses and emotions. How Curiosity Styles Shape Wikipedia Use and Learning
 A study of global Wikipedia browsing patterns reveals three curiosity styles: the focused "hunter," the exploratory "busybody," and the creative "dancer." Data from 482,760 readers in 50 countries shows that cultural factors, such as gender equality and education levels, influence browsing styles, with more egalitarian countries showing greater exploratory browsing.
A study of global Wikipedia browsing patterns reveals three curiosity styles: the focused "hunter," the exploratory "busybody," and the creative "dancer." Data from 482,760 readers in 50 countries shows that cultural factors, such as gender equality and education levels, influence browsing styles, with more egalitarian countries showing greater exploratory browsing. Depression Alters Brain Circuits, Heightening Negative Perception
 Scientists have identified how depression alters the brain’s response to positive and negative stimuli, particularly in the amygdala, a key emotional processing center. The study found that depression reduces neural activity linked to positive perceptions while increasing it for negative perceptions.
Scientists have identified how depression alters the brain’s response to positive and negative stimuli, particularly in the amygdala, a key emotional processing center. The study found that depression reduces neural activity linked to positive perceptions while increasing it for negative perceptions. Youth Face Rising Risks of Harassment and Exploitation in the Metaverse
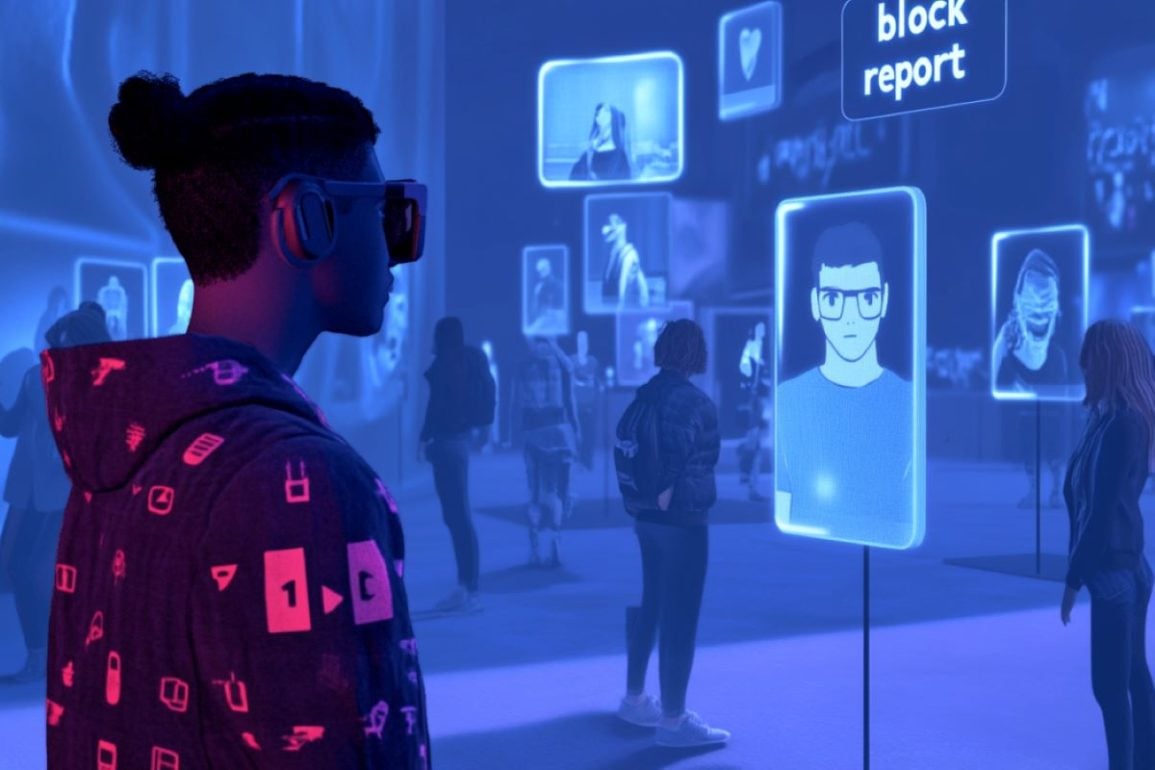 A new study reveals that youth are vulnerable to various forms of harm in the metaverse, including bullying, harassment, and sexual exploitation. Using data from over 5,000 U.S. teens, researchers found significant incidents of hate speech, sexual harassment, and grooming behavior in virtual reality (VR) spaces.
A new study reveals that youth are vulnerable to various forms of harm in the metaverse, including bullying, harassment, and sexual exploitation. Using data from over 5,000 U.S. teens, researchers found significant incidents of hate speech, sexual harassment, and grooming behavior in virtual reality (VR) spaces. Social Media Verification Drives Polarization and Echo Chambers
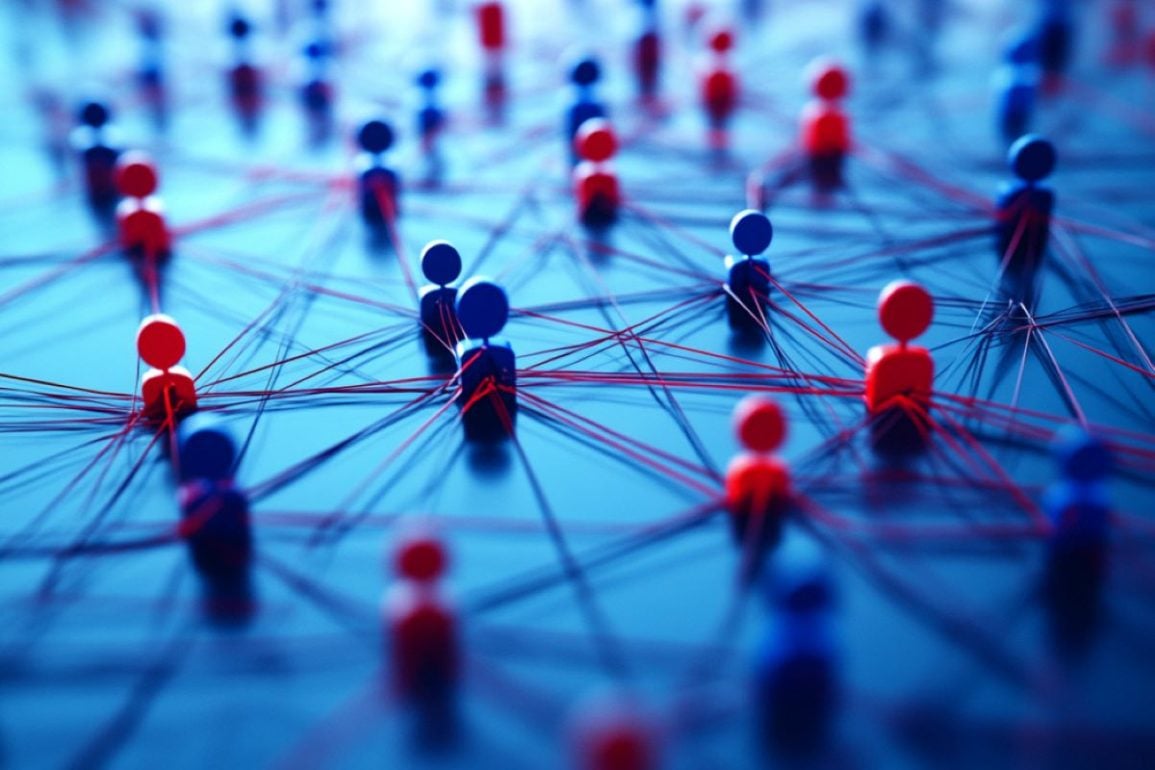 A new study shows that X's verification system, which gives verified users priority in algorithms, can increase polarization and trigger the formation of echo chambers. Researchers used computational modeling to simulate how verified users affect the spread of political opinions on social media. They found that when verified users with entrenched opinions post, their influence can drive polarization, while centrist ideologues can reduce it if present in sufficient numbers.
A new study shows that X's verification system, which gives verified users priority in algorithms, can increase polarization and trigger the formation of echo chambers. Researchers used computational modeling to simulate how verified users affect the spread of political opinions on social media. They found that when verified users with entrenched opinions post, their influence can drive polarization, while centrist ideologues can reduce it if present in sufficient numbers. Emotional Blindness Drives Empathy Deficits in Psychopathy
 A new study links psychopathy with alexithymia, or emotional blindness, which may explain the emotional deficits seen in people with psychopathic traits. Individuals with strong psychopathic traits struggle to recognize and describe their emotions, which affects their ability to show empathy and regulate emotions.
A new study links psychopathy with alexithymia, or emotional blindness, which may explain the emotional deficits seen in people with psychopathic traits. Individuals with strong psychopathic traits struggle to recognize and describe their emotions, which affects their ability to show empathy and regulate emotions.