Discord launches end-to-end encrypted voice and video chats
Discord will now offer audio and video calls that even the company won't be able to listen in on.
© 2024 TechCrunch. All rights reserved. For personal use only.
Discord will now offer audio and video calls that even the company won't be able to listen in on.
© 2024 TechCrunch. All rights reserved. For personal use only.
The U.K.’s data protection watchdog claims a crackdown on websites that don’t ask for consent from visitors to track and profile their activity for ad targeting is bearing fruit. However it’s admitted some of the changes driven by the intervention have seen sites adopting a controversial type of paywall that demands users pay a fee […]
© 2024 TechCrunch. All rights reserved. For personal use only.
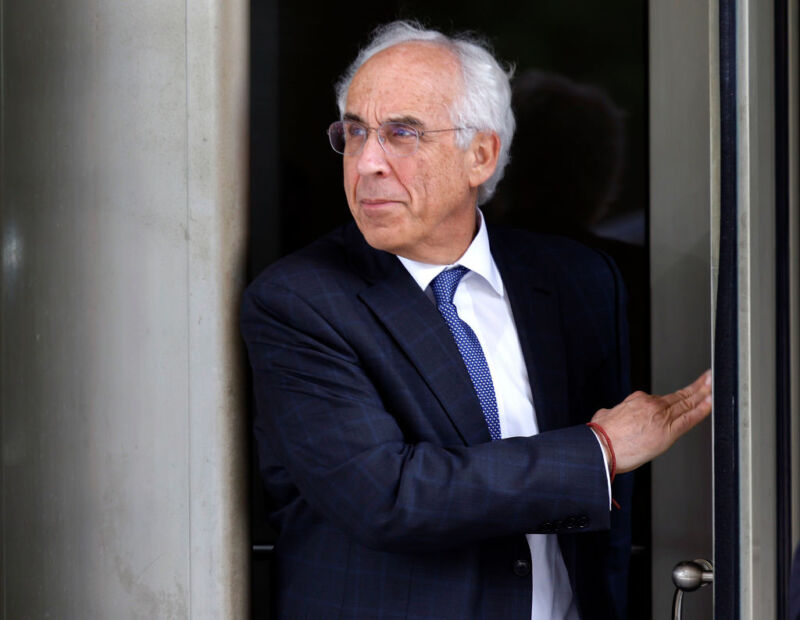

Enlarge / Andrew J. Pincus, attorney for TikTok and ByteDance, leaves the E. Barrett Prettyman US Court House with members of his legal team as the US Court of Appeals hears oral arguments in the case TikTok Inc. v. Merrick Garland on September 16 in Washington, DC. (credit: Kevin Dietsch / Staff | Getty Images News)
The fight to keep TikTok operating unchanged in the US reached an appeals court Monday, where TikTok and US-based creators teamed up to defend one of the world's most popular apps from a potential US ban.
TikTok lawyer Andrew Pincus kicked things off by warning a three-judge panel that a law targeting foreign adversaries that requires TikTok to divest from its allegedly China-controlled owner, ByteDance, is "unprecedented" and could have "staggering" effects on "the speech of 170 million Americans."
Pincus argued that the US government was "for the first time in history" attempting to ban speech by a specific US speaker—namely, TikTok US, the US-based entity that allegedly curates the content that Americans see on the app.



Google’s lead privacy regulator in the European Union has opened an investigation into whether or not it has complied with the bloc’s data protection laws in relation to use of people’s information for training generative AI. Specifically it’s looking into whether the tech giant needed to carry out a data protection impact assessment (DPIA) in […]
© 2024 TechCrunch. All rights reserved. For personal use only.

Het bericht Telegram modereert privégesprekken toch niet verscheen eerst op DutchCowboys.

 Cloud Monitor by ManagedMethods is a cloud security solution specifically tailored for technology teams working in the education market. As schools strive to create safe and enriching digital learning environments for students and educators alike, Cloud Monitor stands as the vanguard of cloud security, ensuring data protection and privacy in the ever-evolving edtech space.
Cloud Monitor by ManagedMethods is a cloud security solution specifically tailored for technology teams working in the education market. As schools strive to create safe and enriching digital learning environments for students and educators alike, Cloud Monitor stands as the vanguard of cloud security, ensuring data protection and privacy in the ever-evolving edtech space.
At the forefront of innovation, Cloud Monitor harnesses the power of AI-driven technology to provide visibility and control into cloud applications, thereby detecting and thwarting potential security threats. As education embraces the cloud to foster collaborative and flexible learning experiences, safeguarding sensitive student and financial data is critical. Cloud Monitor empowers districts to fulfill their duty of care, securing data while fostering a climate of trust among students, educators, and parents.
Implementing Cloud Monitor is easy, thanks to its user-friendly design and seamless integration with Google Workspace and Microsoft 365, it requires minimal training. It’s automated alerts and remediation capabilities enables swift action against any potential breaches, malware attacks, or student safety risks, freeing district technology teams to focus on the million other things they have on their to-do list.
With the ever-evolving data privacy landscape, adhering to industry standards and regulations such as COPPA, FERPA, and a variety of state-level regulations is a must. Cloud Monitor assists districts in maintaining compliance, monitoring data, and detecting policy violations.
Cloud Monitor by ManagedMethods is the ultimate guardian of cloud security and safety for K-12 schools, empowering districts to create safe, secure, and compliant cloud learning environments. For these reasons and more, Cloud Monitor by ManagedMethods is a Cool Tool Award Winner for “Best Security (Cybersecurity, Student safety) Solution” as part of The EdTech Awards 2024 from EdTech Digest. Learn more.
The post Cloud Monitor by ManagedMethods appeared first on EdTech Digest.
When Los Angeles Unified School District launched a districtwide AI chatbot nicknamed “Ed” in March, officials boasted that it represented a revolutionary new tool that was only possible thanks to generative AI — a personal assistant that could point each student to tailored resources and assignments and playfully nudge and encourage them to keep going.
But last month, just a few months after the fanfare of the public launch event, the district abruptly shut down its Ed chatbot, after the company it contracted to build the system, AllHere Education, suddenly furloughed most of its staff citing financial difficulties. The company had raised more than $12 million in venture capital, and its five-year contract with the LA district was for about $6 million over five years, about half of which the company had already been paid.
It’s not yet clear what happened: LAUSD officials declined interview requests from EdSurge, and officials from AllHere did not respond to requests for comment about the company’s future. A statement issued by the school district said “several educational technology companies are interested in acquiring” AllHere to continue its work, though nothing concrete has been announced.
A tech leader for the school district, which is the nation’s second-largest, told the Los Angeles Times that some information in the Ed system is still available to students and families, just not in chatbot form. But it was the chatbot that was touted as the key innovation — which relied on human moderators at AllHere to monitor some of the chatbot’s output who are no longer actively working on the project.
Some edtech experts contacted by EdSurge say that the implosion of the cutting-edge AI tool offers lessons for other schools and colleges working to make use of generative AI. Most of those lessons, they say, center on a factor that is more difficult than many people realize: the challenges of corralling and safeguarding data.
When leaders from AllHere gave EdSurge a demo of the Ed chatbot in March, back when the company seemed thriving and had recently been named to a Time magazine list of the “World’s Top Edtech Companies of 2024,” company leaders were most proud of how the chatbot cut across dozens of tech tools that the school system uses.
“The first job of Ed was, how do you create one unified learning space that brings together all the digital tools, and that eliminates the high number of clicks that otherwise the student would need to navigate through them all?” the company’s then-CEO, Joanna Smith-Griffin, said at the time. (The LAUSD statement said she is no longer with the company.)
Such data integration had not previously been a focus of the company, though. The company’s main expertise was making chatbots that were “designed to mimic real conversations, responding with empathy or humor depending on the student's needs in the moment on an individual level,” according to its website.
Michael Feldstein, a longtime edtech consultant, said that from the first time he heard about the Ed chatbot, he saw the project as too ambitious for a small startup to tackle.
“In order to do the kind of work that they were promising, they needed to gather information about students from many IT systems,” he said. “This is the well-known hard part of edtech.”
Feldstein guesses that to make a chatbot that could seamlessly take data from nearly every critical learning resource at a school, as announced at the splashy press conference in March, it could take 10 times the amount AllHere was being paid.
“There’s no evidence that they had experience as system integrators,” he said of AllHere. “It’s not clear that they had the expertise.”
In fact, a former engineer from AllHere reportedly sent emails to leaders in the school district warning that the company was not handling student data according to best practices of privacy protection, according to an article in The 74, the publication that first reported the implosion of AllHere. The official, Chris Whiteley, reportedly told state and district officials that the way the Ed chatbot handled student records put the data at risk of getting hacked. (The school district’s statement defends its privacy practices, saying that: “Throughout the development of the Ed platform, Los Angeles Unified has closely reviewed the platform to ensure compliance with applicable privacy laws and regulations, as well as Los Angeles Unified’s own data security and privacy policies, and AllHere is contractually obligated to do the same.”)
LAUSD’s data systems have recently faced breaches that appear unrelated to the Ed chatbot project. Last month hackers claimed to be selling troves of millions of records from LAUSD on the dark web for $1,000. And a data breach of a data warehouse provider used by LAUSD, Snowflake, claims to have snatched records of millions of students, including from the district. A more recent breach of Snowflake may have affected LAUSD or other tech companies it works with as well.
“LAUSD maintains an enormous amount of sensitive data. A breach of an integrated data system of LAUSD could affect a staggering number of individuals,” said Doug Levin, co-founder and national director of the K12 Security Information eXchange, in an email interview. He said he is waiting for the district to share more information about what happened. “I am mostly interested in understanding whether any of LAUSD’s edtech vendors were breached and — if so — if other customers of those vendors are at risk,” he said. “This would make it a national issue.”
Meanwhile, what happens to all the student data in the Ed chatbot?
According to the statement released by LAUSD: “Any student data belonging to the District and residing in the Ed platform will continue to be subject to the same privacy and data security protections, regardless of what happens to AllHere as a company.”
A copy of the contract between AllHere and LAUSD, obtained by EdSurge under a public records request, does indicate that all data from the project “will remain the exclusive property of LAUSD.” And the contract contains a provision stating that AllHere “shall delete a student’s covered information upon request of the district.”
Related document: Contract between LAUSD and AllHere Education.Rob Nelson, executive director for academic technology and planning at the University of Pennsylvania, said the situation does create fresh risks, though.
“Are they taking appropriate technical steps to make sure that data is secure and there won’t be a breach or something intentional by an employee?” Nelson wondered.
James Wiley, a vice president at the education market research firm ListEdTech, said he would have advised AllHere to seek a partner with experience wrangling and managing data.
When he saw a copy of the contract between the school district and AllHere, he said his reaction was, “Why did you sign up for this?,” adding that “some of the data you would need to do this chatbot isn’t even called out in the contract.”
Wiley said that school officials may not have understood how hard it was to do the kind of data integration they were asking for. “I think a lot of times schools and colleges don’t understand how complex their data structure is,” he added. “And you’re assuming a vendor is going to come in and say, ‘It’s here and here.’” But he said it is never that simple.
“Building the Holy Grail of a data-informed, personalized achievement tool is a big job,” he added. “It’s a noble cause, but you have to realize what you have to do to get there.”
For him, the biggest lesson for other schools and colleges is to take a hard look at their data systems before launching a big AI project.
“It’s a cautionary tale,” he concluded. “AI is not going to be a silver bullet here. You’re still going to have to get your house in order before you bring AI in.”
To Nelson, of the University of Pennsylvania, the larger lesson in this unfolding saga is that it’s too soon in the development of generative AI tools to scale up one idea to a whole school district or college campus.
Instead of one multimillion-dollar bet, he said, “let’s invest $10,000 in five projects that are teacher-based, and then listen to what the teachers have to say about it and learn what these tools are going to do well.”


© Thomas Bethge / Shutterstock

Microsoft recently caught state-backed hackers using its generative AI tools to help with their attacks. In the security community, the immediate questions weren’t about how hackers were using the tools (that was utterly predictable), but about how Microsoft figured it out. The natural conclusion was that Microsoft was spying on its AI users, looking for harmful hackers at work.
Some pushed back at characterizing Microsoft’s actions as “spying.” Of course cloud service providers monitor what users are doing. And because we expect Microsoft to be doing something like this, it’s not fair to call it spying.
We see this argument as an example of our shifting collective expectations of privacy. To understand what’s happening, we can learn from an unlikely source: fish.
In the mid-20th century, scientists began noticing that the number of fish in the ocean—so vast as to underlie the phrase “There are plenty of fish in the sea”—had started declining rapidly due to overfishing. They had already seen a similar decline in whale populations, when the post-WWII whaling industry nearly drove many species extinct. In whaling and later in commercial fishing, new technology made it easier to find and catch marine creatures in ever greater numbers. Ecologists, specifically those working in fisheries management, began studying how and when certain fish populations had gone into serious decline.
One scientist, Daniel Pauly, realized that researchers studying fish populations were making a major error when trying to determine acceptable catch size. It wasn’t that scientists didn’t recognize the declining fish populations. It was just that they didn’t realize how significant the decline was. Pauly noted that each generation of scientists had a different baseline to which they compared the current statistics, and that each generation’s baseline was lower than that of the previous one.
What seems normal to us in the security community is whatever was commonplace at the beginning of our careers.
Pauly called this “shifting baseline syndrome” in a 1995 paper. The baseline most scientists used was the one that was normal when they began their research careers. By that measure, each subsequent decline wasn’t significant, but the cumulative decline was devastating. Each generation of researchers came of age in a new ecological and technological environment, inadvertently masking an exponential decline.
Pauly’s insights came too late to help those managing some fisheries. The ocean suffered catastrophes such as the complete collapse of the Northwest Atlantic cod population in the 1990s.
Internet surveillance, and the resultant loss of privacy, is following the same trajectory. Just as certain fish populations in the world’s oceans have fallen 80 percent, from previously having fallen 80 percent, from previously having fallen 80 percent (ad infinitum), our expectations of privacy have similarly fallen precipitously. The pervasive nature of modern technology makes surveillance easier than ever before, while each successive generation of the public is accustomed to the privacy status quo of their youth. What seems normal to us in the security community is whatever was commonplace at the beginning of our careers.
Historically, people controlled their computers, and software was standalone. The always-connected cloud-deployment model of software and services flipped the script. Most apps and services are designed to be always-online, feeding usage information back to the company. A consequence of this modern deployment model is that everyone—cynical tech folks and even ordinary users—expects that what you do with modern tech isn’t private. But that’s because the baseline has shifted.
AI chatbots are the latest incarnation of this phenomenon: They produce output in response to your input, but behind the scenes there’s a complex cloud-based system keeping track of that input—both to improve the service and to sell you ads.
Shifting baselines are at the heart of our collective loss of privacy. The U.S. Supreme Court has long held that our right to privacy depends on whether we have a reasonable expectation of privacy. But expectation is a slippery thing: It’s subject to shifting baselines.
The question remains: What now? Fisheries scientists, armed with knowledge of shifting-baseline syndrome, now look at the big picture. They no longer consider relative measures, such as comparing this decade with the last decade. Instead, they take a holistic, ecosystem-wide perspective to see what a healthy marine ecosystem and thus sustainable catch should look like. They then turn these scientifically derived sustainable-catch figures into limits to be codified by regulators.
In privacy and security, we need to do the same. Instead of comparing to a shifting baseline, we need to step back and look at what a healthy technological ecosystem would look like: one that respects people’s privacy rights while also allowing companies to recoup costs for services they provide. Ultimately, as with fisheries, we need to take a big-picture perspective and be aware of shifting baselines. A scientifically informed and democratic regulatory process is required to preserve a heritage—whether it be the ocean or the Internet—for the next generation.
