Emerging research suggests that chronic inflammation, rather than neurotransmitter deficiencies alone, may be a major factor behind depression, reshaping traditional views of the condition. This insight links inflammation, both in the body and brain, to depressive symptoms, explaining why some patients don't respond to conventional antidepressants. Studies reveal that stress can trigger immune responses that activate and later damage microglial cells in the brain, worsening depressive symptoms over time.
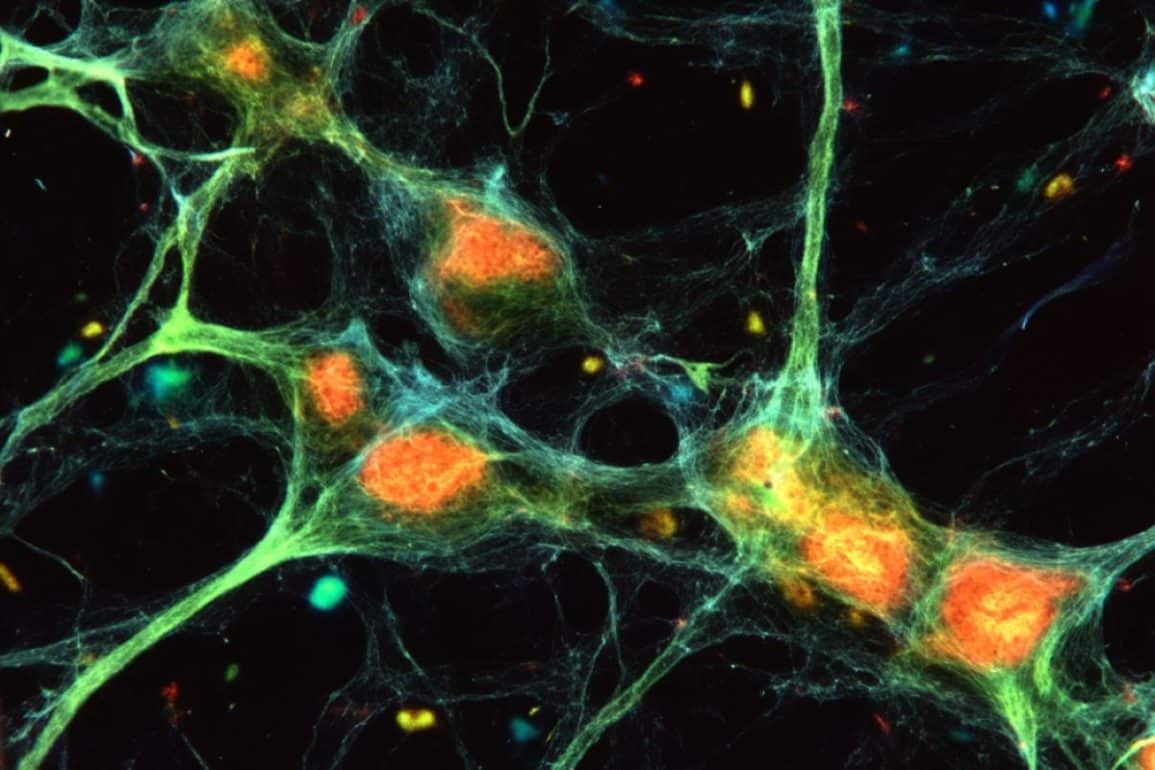 New research highlights neuroglia (or glia cells) as critical players in mental health, potentially influencing conditions like depression and schizophrenia. Glia cells, long considered "support cells" in the brain, have now been shown to communicate through unique calcium signaling, impacting neuronal function and stress responses. Studies suggest that compromised astrocyte function, a glial cell type, may relate to depressive symptoms and schizophrenia.
New research highlights neuroglia (or glia cells) as critical players in mental health, potentially influencing conditions like depression and schizophrenia. Glia cells, long considered "support cells" in the brain, have now been shown to communicate through unique calcium signaling, impacting neuronal function and stress responses. Studies suggest that compromised astrocyte function, a glial cell type, may relate to depressive symptoms and schizophrenia.