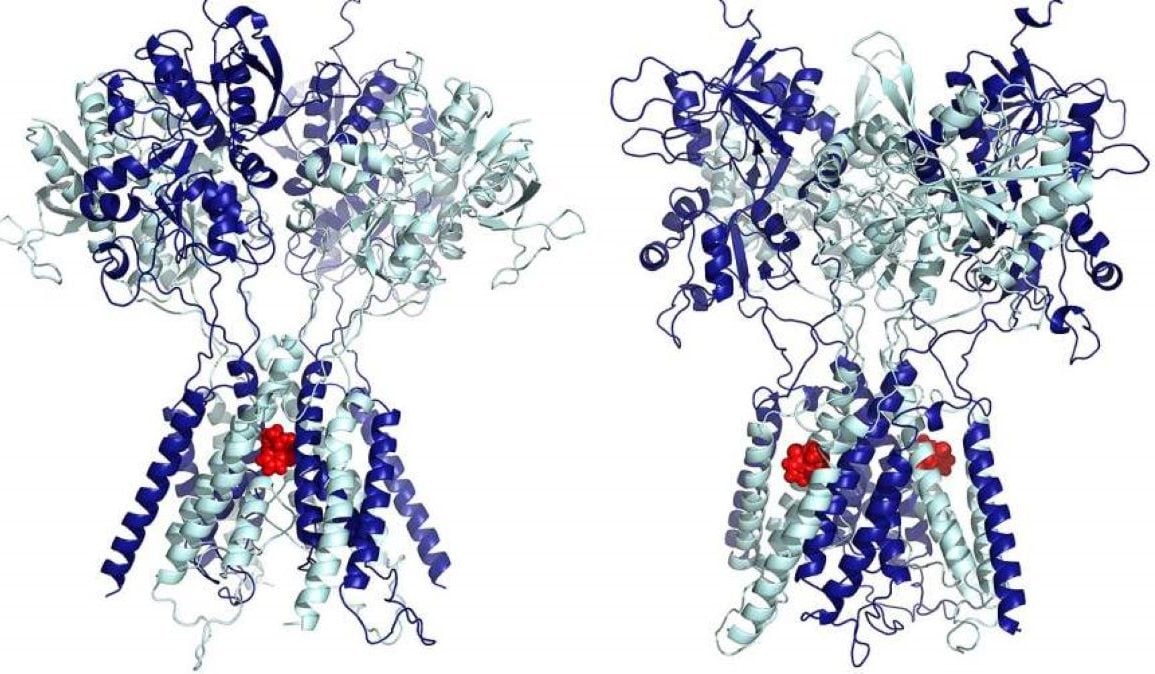
 Researchers have identified how low-dose ketamine alleviates depression by selectively targeting specific NMDA receptors in the brain. Unlike high-dose anesthetic effects, low-dose ketamine binds to lateral grooves on NMDA receptors, enhancing excitatory transmission and long-term synaptic changes.
Researchers have identified how low-dose ketamine alleviates depression by selectively targeting specific NMDA receptors in the brain. Unlike high-dose anesthetic effects, low-dose ketamine binds to lateral grooves on NMDA receptors, enhancing excitatory transmission and long-term synaptic changes. Reading view
Beer Drinkers Have Poorer Diets, Lower Activity Levels
 Beer-only drinkers have the lowest diet quality, highest caloric intake, and lowest physical activity levels compared to those who drink wine, liquor, or a combination. Researchers analyzed over 1,900 U.S. adults and found beer drinkers scored lowest on the Healthy Eating Index, while wine drinkers scored highest.
Beer-only drinkers have the lowest diet quality, highest caloric intake, and lowest physical activity levels compared to those who drink wine, liquor, or a combination. Researchers analyzed over 1,900 U.S. adults and found beer drinkers scored lowest on the Healthy Eating Index, while wine drinkers scored highest. Microbial Load, Not Disease, Shapes Gut Microbiome Signatures
 A new study reveals that changes in gut microbial load, influenced by factors like diet, age, and antibiotics, drive the presence of bacteria previously linked to diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. Using a machine learning model, researchers found that microbial load variations explained bacterial signatures in patients' microbiomes more strongly than the diseases themselves.
A new study reveals that changes in gut microbial load, influenced by factors like diet, age, and antibiotics, drive the presence of bacteria previously linked to diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer. Using a machine learning model, researchers found that microbial load variations explained bacterial signatures in patients' microbiomes more strongly than the diseases themselves. Traditional Paranormal Beliefs Linked to Stress
 Traditional paranormal beliefs, such as witchcraft and religious superstition, are linked to higher stress and reduced coping ability, while new age beliefs, like spiritualism and precognition, show no such link. Researchers used an improved scale to analyze responses from over 3,000 participants, revealing that traditional beliefs may reflect anxieties about external control. The findings highlight the psychological differences between belief types but cannot confirm cause-and-effect relationships.
Traditional paranormal beliefs, such as witchcraft and religious superstition, are linked to higher stress and reduced coping ability, while new age beliefs, like spiritualism and precognition, show no such link. Researchers used an improved scale to analyze responses from over 3,000 participants, revealing that traditional beliefs may reflect anxieties about external control. The findings highlight the psychological differences between belief types but cannot confirm cause-and-effect relationships. Study Revolutionize Restless Legs Syndrome Treatment
 Researchers released new clinical guidelines for treating restless legs syndrome (RLS), emphasizing patient-centered care and evidence-based updates. Iron supplementation is now a key recommendation, addressing low brain iron as a cause of RLS. Dopamine agonists like pramipexole and ropinirole are de-emphasized due to risks of worsening symptoms, while newer treatments such as alpha-2-delta ligands, nerve stimulation, and low-dose opioids gain conditional or strong recommendations.
Researchers released new clinical guidelines for treating restless legs syndrome (RLS), emphasizing patient-centered care and evidence-based updates. Iron supplementation is now a key recommendation, addressing low brain iron as a cause of RLS. Dopamine agonists like pramipexole and ropinirole are de-emphasized due to risks of worsening symptoms, while newer treatments such as alpha-2-delta ligands, nerve stimulation, and low-dose opioids gain conditional or strong recommendations. Metabolic Pathways Link Cannabis to Psychosis in Teens
 A study investigated how cannabis use influences metabolomic patterns linked to psychotic-like experiences in adolescents. Blood samples revealed that non-cannabis users showed inflammatory metabolic changes associated with hallucinations, while cannabis users exhibited shifts in energy-related metabolites tied to brain ketogenesis. These findings suggest that cannabis use may trigger distinct molecular pathways in psychotic-like experiences.
A study investigated how cannabis use influences metabolomic patterns linked to psychotic-like experiences in adolescents. Blood samples revealed that non-cannabis users showed inflammatory metabolic changes associated with hallucinations, while cannabis users exhibited shifts in energy-related metabolites tied to brain ketogenesis. These findings suggest that cannabis use may trigger distinct molecular pathways in psychotic-like experiences. Isolation Spurs Teen Threat Sensitivity, Even With Online Interaction
 A new study finds that brief isolation increases threat sensitivity in teens, even if they remain connected online. Adolescents isolated in a room for several hours showed heightened physiological stress and anxious responses to potential threats, regardless of whether they had access to smartphones.
A new study finds that brief isolation increases threat sensitivity in teens, even if they remain connected online. Adolescents isolated in a room for several hours showed heightened physiological stress and anxious responses to potential threats, regardless of whether they had access to smartphones. Are Emotional Sounds Universal Across Languages?
 A new study examined vocal expressions of emotion across 131 languages, exploring similarities in emotional interjections and comparing them to non-linguistic sounds like cries and laughter. The research aimed to understand whether shared vocal patterns exist globally and if these patterns relate to our evolutionary roots in vocal communication. The team found that vocal expressions of pain, like "Ouch!", showed consistent vowel forms across languages, while disgust and joy did not.
A new study examined vocal expressions of emotion across 131 languages, exploring similarities in emotional interjections and comparing them to non-linguistic sounds like cries and laughter. The research aimed to understand whether shared vocal patterns exist globally and if these patterns relate to our evolutionary roots in vocal communication. The team found that vocal expressions of pain, like "Ouch!", showed consistent vowel forms across languages, while disgust and joy did not. AI Model Reveals Shifting Cause-and-Effect in Complex Systems
 A novel machine learning model called Temporal Autoencoders for Causal Inference (TACI) accurately detects changing cause-and-effect relationships in complex, time-varying systems like weather patterns and brain activity. By analyzing both synthetic and real data, TACI captures dynamic interactions and quantifies shifts in strength or direction over time. Tested on long-term weather data and brain imaging in monkeys, TACI successfully pinpointed when causal connections emerged, weakened, or reversed.
A novel machine learning model called Temporal Autoencoders for Causal Inference (TACI) accurately detects changing cause-and-effect relationships in complex, time-varying systems like weather patterns and brain activity. By analyzing both synthetic and real data, TACI captures dynamic interactions and quantifies shifts in strength or direction over time. Tested on long-term weather data and brain imaging in monkeys, TACI successfully pinpointed when causal connections emerged, weakened, or reversed. Could Targeting Genetics Reduce Our Cravings for Sugary Foods?
 A new study has revealed how genetic variations in the SI gene, which affects sucrose digestion, influence dietary preferences and intake of sugary foods. Researchers found that individuals with limited sucrose-digesting ability, due to specific genetic variations, showed reduced sugar cravings and consumption. This discovery opens up the potential to develop targeted treatments to reduce sugar intake on a population level, potentially reducing the incidence of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
A new study has revealed how genetic variations in the SI gene, which affects sucrose digestion, influence dietary preferences and intake of sugary foods. Researchers found that individuals with limited sucrose-digesting ability, due to specific genetic variations, showed reduced sugar cravings and consumption. This discovery opens up the potential to develop targeted treatments to reduce sugar intake on a population level, potentially reducing the incidence of obesity and type 2 diabetes. How Viewing Dogs as Family Changes Owner Behaviors
 New research shows that how owners perceive their dogs—as friends, family, or security guards—shapes the way they care for them. Surveying over 800 dog owners, researchers found that people who view dogs as family often form closer bonds and dedicate more time to them, while others keep dogs mainly for companionship or practical roles. This generational shift in perception highlights a growing trend of treating dogs as family members.
New research shows that how owners perceive their dogs—as friends, family, or security guards—shapes the way they care for them. Surveying over 800 dog owners, researchers found that people who view dogs as family often form closer bonds and dedicate more time to them, while others keep dogs mainly for companionship or practical roles. This generational shift in perception highlights a growing trend of treating dogs as family members. Psychedelic Therapy Could Benefit 5.6 Million People with Depression
 Psilocybin-assisted therapy could potentially benefit up to 5.6 million Americans with major depressive disorder or treatment-resistant depression, offering a powerful alternative to traditional treatments. Researchers applied medical criteria to a national pool of patients and found that over half might be eligible for psilocybin therapy, pending FDA approval. If approved, this therapy could significantly impact public health policies, insurance frameworks, and economic costs by reducing reliance on long-term antidepressant prescriptions.
Psilocybin-assisted therapy could potentially benefit up to 5.6 million Americans with major depressive disorder or treatment-resistant depression, offering a powerful alternative to traditional treatments. Researchers applied medical criteria to a national pool of patients and found that over half might be eligible for psilocybin therapy, pending FDA approval. If approved, this therapy could significantly impact public health policies, insurance frameworks, and economic costs by reducing reliance on long-term antidepressant prescriptions. Study Links Stress Hormones to Diabetes
 New research suggests that stress hormones, rather than impaired insulin signaling, may primarily drive diabetes in obesity. This study found that high levels of stress hormones, like norepinephrine, counter insulin’s effects, leading to insulin resistance even with intact insulin signaling. When genetically modified mice couldn’t produce these stress hormones, they avoided diabetes despite obesity. This breakthrough may explain why some obese individuals develop diabetes while others don’t.
New research suggests that stress hormones, rather than impaired insulin signaling, may primarily drive diabetes in obesity. This study found that high levels of stress hormones, like norepinephrine, counter insulin’s effects, leading to insulin resistance even with intact insulin signaling. When genetically modified mice couldn’t produce these stress hormones, they avoided diabetes despite obesity. This breakthrough may explain why some obese individuals develop diabetes while others don’t. 




